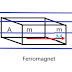
MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF MATTER
INTENSITY
OF MAGNETIZATION:
-
If a
magnetic material (ferromagnetic substance) be kept in magnetic field, the
material get magnetized and a magnetic moment get induced. The magnetic moment
so induced per unit volume is called intensity of magnetization
H – Magnetizing
field (external field)
M = m × 2l
Volume of
the material = A × 2l
Intensity of
magnetization, I = M/volume = m/A
MAGNETIC SUSCEPTIBLITY:
-
The magnetic
susceptibility refers the ability of the material that to what extent the
material can be magnetized by using magnetizing field. If constant magnetic
field be given to two different material, the material having the greater
susceptibility will have the greater magnetization.
It is observed that the intensity of magnetization depends directly on
the magnetizing field.
I ∞ H
Or, I = ꭙH
Where, ꭙ is the magnetic
susceptibility.
MAGNETIC INDUCTION:
-
If a magnetic material be kept in
magnetizing field, magnetic moment gets induced and certain magnetic line of
the force will pass through the material. The magnetic induction is the total
no. of magnetic line of force passes through the material per unit area.
H – given magnetic field intensity
GAUSS’s Law of Magnetization says that
4π lines are associated with unit pole strength.
B = H + 4πm/A (for
Ferro or Para)
= H + 4πI
B = H -
4πm/A ( for Dia)
= H - 4πI
Magnetic permeability: -
It is the ratio of magnetic line of force when a specimen be
kept in magnetizing field to the no. of line of force when there is no material
µ = B/H
MAGNETIC MATERIALS
1) DIAMAGNETIC SUBSTANCE: -
These substances are repelled by
magnet, atoms possess paired electrons.
PROPERTY
A) If a diamagnetic substance be kept in
non-uniform magnetic field, it moves from the region of strong magnetic field
to the region of weak magnetic field.
Potential Energy of a magnetic
dipole
U = MBCosθ
Angle between M and B
i.e. θ = 180
U = MB
Every body try to be posses minimum P.E.
So B should be minimum
A)
The
susceptibility is -ve.
B)
Magnetic
permeability is less than one.
C)
The
Diamagnetic substance losses its magnetic property immediately after removing
the field.
D)
The
magnetic property of diamagnetic substances is independent of temperature.
B) PARAMAGNETIC SUBSTANCE: -
Thee substances are attracted by
magnet but very feebly. The atoms possess unpaired electrons.
PROPERTIES
a) If a paramagnetic substance be kept in non –
uniform magnetic fields, it moves from the region of weak magnetic field to the
region of strong magnetic field.
P.E. of a magnetic dipole,
U = - MBCosθ
Angle between M
and B i.e. θ = 0
U = - MB
Every body try to be possess minimum P.E.
So,
B should be maximum.
b) The susceptibility is +ve.
c) Magnetic permeability is greater than
one.
d) The Paramagnetic substance losses its
magnetic property immediately after removing the field.
e) The magnetic property of diamagnetic
substances is independent of temperature.
I ∞ 1/T
B) FERROMAGNETIC SUBSTACE: -
These Substances are strongly
attracted by magnet. Some of the paramagnetic substances which having strong
magnetism are separately called Ferromagnetic substances because ferrum is the
strongest of all Iron, Nickel, Cobalt, Gadalinium, Dysposium are the
Ferromagnetic substance
PROPERTIES
a)
If a ferromagnetic substance be kept in non –
uniform magnetic fields, it moves from the region of weak magnetic field to the
region of strong magnetic field.
P.E. of a magnetic dipole,
U = - MBCosθ
Angle between M and B
i.e. θ = 0
U = - MB
Every body try to be possess minimum P.E.
So,
B should be maximum.
b) The susceptibility is more +ve.
c) Magnetic permeability is much greater
than one.
d) The ferromagnetic substance does not losses
its magnetic property immediately after removing the field.
e) The magnetic property of diamagnetic
substances is independent of temperature.
I ∞ 1/T
2) A CURRENT CARRYING LOOP BEHAVES AS A MAGNETIC DIPOLE:
-
If a bar magnet be kept in magnetic field,
torque acts on the magnet is
Ⴀ
= MBSin θ……………………………………….(1)
Similarly,
if a current carrying loop be kept in magnetic field, Torque act on it is-
Ⴀ
= BIASin θ……………………………………….(2)
Comparing (1) and (2), we get
Magnetic Moment,
M = IA
= Current × Area
Let an electron revolve in an orbit of radius ‘r’ with
velocity v
M = I × A
But v = r ω
i.e. ω = v/r
M = e v r/2
Multiplying and dividing by ‘m’
Where L = m v r is called angular momentum
From Bohr’s theory of stationary non –
radiation orbit
mvr(L) = nh/2π
M = e × nh/2πm
= n (eh/4πm)
If n = 1 (Least
value)
(Bohr’s magneton)